Md.Shafiul Azam
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Bangladesh
Title: A bioinspired strategy for immobilizing silver nanoparticles towards the synthesis of antimicrobial paper
Biography
Biography: Md.Shafiul Azam
Abstract
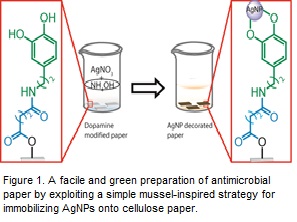
Statement of the Problem: Antimicrobial materials based on various nanoparticles has attracted huge attention in last few decades because of the cheapness, easiness to use, and effectiveness in preventing annexation and proliferation of microbes on material surfaces. Paper has been used in many applications as a matrix to carry the nanoparticles due to its high porosity, considerable mechanical strength, and high availability. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have widely been used as antibacterial/antifungal agents in a varied range of consumer products because of their large active surface area. However, effective methods for immobilizing AgNPs on cellulose paper or similar surfaces for various applications are inadequately advanced. Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: By exploiting a novel and simple mussel-inspired strategy here we present our method for immobilizing AgNPs on paper. First, we modified cellulose paper with dopamine molecules by a simple, efficient, and environmentally friendly approach. The dopamine molecules possess excellent adhesion and strong coordination with metal substrates through catechol groups offering a potentially robust interface between AgNPs and organic structure of paper. Next, AgNPs are deposited onto the paper by simply immersing dopamine modified paper in silver salt solution to attain the antimicrobial properties. Findings: The SEM study of the synthesized antimicrobial papers confirmed that the loading of AgNPs was time dependent and the average size of the nanoparticles became 50-60 nm after 12 h of deposition time. FTIR and XPS analysis of the paper modified at each steps revealed the introduction of new functional groups through the synthesis. The mechanical strength of the paper measured as similar as fresh filter paper by using an universal testing machine will also be presented. Conclusion & Significance: The paper decorated with AgNPs showed excellent antimicrobial activity against highly virulent and multiple antibiotics resistant gram positive and gram negative bacteria. It also showed antifungal activity against some extremely virulent fungal species.