Theme: “Innovation in Material Science & Biomaterialsâ€
Emerging Materials 2021
Emerging materials 2021 is a unique event and platform for global scientists, researchers, directors, professors, engineers from the research areas of Materials Science, Nanotechnology, Chemistry and Physics to share their knowledge and research experiences with interactive panel discussion and sessions by Keynote Lectures, Oral Presentations, and Poster Presentation. The scientific sessions will comprise research areas of Advanced Materials, Polymer Science, Materials Science, Nanotechnology, Tissue Engineering, Carbon Materials, Energy Materials, Biopolymers, 3D Printing, Ceramics, Conductive Materials, Electrical, Optical and Magnetic Materials, Materials Applications, etc.
All Academia and Business Companies find the fantastic opportunity to collaborate and access the New Technologies, sharing the knowledge across the globe.
Emerging Materials 2021 provides best opportunity for delegates from various Institutes and Universities to interact with superlative scientists and Materials experts worldwide. The Emerging Materials is anticipated to be the significant world-shattering force that results in influencing the human life and economy.
| Conference Name | Venue | Dates |
|---|---|---|
| Emerging Materials 2021 | Webinar | July 27, 2021 |
Track 1: Emerging Materials and Technology
As the universe require for energy is predicted to still enlarge at a rapid rate, it's critical that enhanced technologies for the sustainably producing, converting and storing energy are developed. Materials are key roadblocks to improved performance during variety of important energy technologies including energy storage in batteries and super-capacitors and energy conversion through solar cells, fuel cells, and thermoelectric devices.
·Sensors based on emerging devices
·Advanced Materials for energy
·Thermoelectric materials
·Transparent Conductors
·Memory Devices
·Chemical Sensor
Track 2: Materials Science and Engineering
Materials Science and engineering is an interdisciplinary study of all materials from glass to those used in aircrafts, which combines extensive natural and manufactured materials that relays the extraction, synthesis, properties, structural characterization, its performance and material processing. Generally, materials are classified into two major divisions as crystalline and non-crystalline materials. The engineering of materials has progression in healthcare industries, medical devices, electronics and photonics, transportation, energy industries as batteries and fuel cells, and nanotechnology. The emerging technologies in materials science comprise of energy materials, nanomaterial, biomaterials, graphene, fullerene, conductive polymers, superalloy, carbon Nanotubes, etc.
-
Materials Synthesis
-
Quantum Materials
-
Novel Materials, Multifunctional Materials
-
Transistor gate materials
-
Photovoltaic
-
Magnetic Materials
-
Fracture analysis
-
Materials in the field of Medicine
-
Materials Characterization
-
Materials – Computational Methods
-
Materials Processing
-
Materials Innovation and Development
Track 3: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is well-defined as handling of matter on atomic, molecular, and supermolecular scale. Earlier, the Nanotechnology was defined as the area of employing atoms and molecules to produce nanoscale products, which are also referred to as molecular nanotechnology. The National Nanotechnology initiative, has defined nanotechnology as the management of material .They are the building blocks of applied nanotechnology. Nanomaterials have led to the production of several materials with the help of Interface and colloid science such as carbon nanotubes, nanorod, fullerene
and nanoparticles as well as the properties of nanomaterials differ from those of bulk materials due to their exceptional optical, electronic and mechanical properties.
-
Nanobiotechnology
-
Nanobiotechnology
-
Nanotechnology for Energy and the Environment
-
Risks and Regulation of Nanotechnology
-
Nanocharacterization & Nanomanufacturing
-
Medical and Science Nanotechnology
Track 4: Materials for Regenerative Medicine, Drug delivery and Cosmetics
The field of regenerative medicine has tremendous potential for improved treatment outcomes and it has been stimulated by advances made in bioengineering over the couple of decades. This techniques is used to combine biometic materials, cells, and bioactive molecules play a decisive role in promoting the regeneration of damaged tissues or as therapeutic systems. The strategies of engineering tissues and assembling functional constructs that they're capable of restoring, revitalizing and retaining lost tissues and organs have impacted the entire spectrum.
-
Hydrogels Implementation
-
Cosmetic Materials
-
Materials in medicine
-
Materials Biology
-
Materials for Drug Delivery
Track 5: Advanced Materials
The exploration on Materials science and engineering, implies a novel group of materials with its individual logic of effect that cannot be defined just in terms of normal classes of heavy , light or form, construction, and surface. The materials like Salmon leather, Wood-Skin flexible wood panel material, Re Wall Naked board, Bling Crete light-reflecting concrete and several other novelties have shaped astonishing and unique characteristics of the materials. Soft materials are additional evolving class that includes gels, colloids, liquids, foams, and coatings. Materials are the core for scientific and industrial advancements of our life.
Track 6: Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering
Biomaterial is defined as a substance that has been engineered to interact with components of living system for both therapeutic and diagnostic purpose. Biomaterials are natural components or it can be synthesized in the laboratory employing metals, ceramics, polymers and composite materials. . The biomaterial science also includes polymer synthesis, drug design, self-assembly of materials, immunology and toxicology. Biomaterials have its wide usage in drug delivery, dental application, surgery and regenerative medicine that mimics the natural function.
-
Nanoelectronics and Quantum nanodevices
-
Nanomedicine and Bionanotechnology
-
Bio-fuels and Bio-energy
-
Tissue Engineering/Regenerative Medicine
-
Single Cell Analysis
-
Cell Manufacturing
-
Shape-memory alloys for biomedical implants
-
Biocompatible polymers for tissue engineering
-
Self-Assembly
-
Self-Assembly Biointerfaces and Biodevices
Track 7: Polymer Science and Technology
Polymer technology is one of the most prevalent zone of existing research as it includes the study and application of nanoscience to polymer-nanoparticle matrices, where nanoparticles are those with at least in dimension of less than 100 nm. Polymer matrix based nanocomposites consist of polymer or copolymer having nanoparticles dispersed in the matrix. Polymer nanotechnology emphases on polymer-based biomaterials, self-assembled polymeric films, nanofabrication of polymers, polymer blends and nanocomposites. Silicon Nano spheres is the extensively known Nano polymer which shows discrete features and harder than silicon. Preceding the age of nanotechnology phase, polymer blends, block copolymer domain frequently attains Nano scale sizes. Some of the natural and synthetic polymers are collagen, enzymes, elastin, cellulose, chitin, plastics, fibers and adhesives.
-
Polymer electronics and photonics
-
Aqueous Coatings
-
Biodegradable Waxes
-
Renewable Hot Melt Adhesives
-
Biodegradable Polymers
-
Nanotechnology in Polymers
-
Nanomaterial-polymer composite materials with superior mechanical properties
-
Polymer-nanomaterial composites
-
Conducting polymers
-
Antifouling polymers
-
3D print manufacturing
Track 8: Advancement of Graphene Physics and 2D Materials
Graphene is the crystalline form of carbon that has two dimensional (2D) properties where it consists of single layer of carbon atom arranged in hexagonal lattice. Graphite which is one of the allotrope of carbon is the softest material with is very good lubricant and is the conductor of electricity. Because of its known unique property, it is being used as thermal insulation. This allotrope of carbon is the basic structure of other allotropes such as diamond, carbon nanotubes, graphite, fullerenes. Carbon Nanotube is the cylindrical form of the allotropes of carbon has unusual thermal conductivity, mechanical and electrical properties and is valuable in the arenas of materials science, nanotechnology, electronic and optics.
-
Carbon nanotubes
-
Graphene and fullerenes
-
Graphene and ultra-tin 2D materials
-
Graphene 3D printing
-
Uses on carbon Nanotubes
-
Graphene The Ultra-Capacitor
-
Graphene devices
-
Acutators
Track 9: Electrical, Optical, Magnetic Materials
Materials which can be magnetized and attracted to a magnet are termed as ferromagnetic materials. Magnetic Smart Materials also have medical applications and it is predictable that they will increase in the future. Magnetic Smart Materials also have medical applications and it is predictable that they will increase in the future. Now-a-days Scientists are also occupied on the advancement of synthetic magnetic particles which can be inoculated into the human body for the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Spintronic, also known as spin electronics or fluxtronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its related magnetic moment, in addition to its vital electronic charge, in solid-state devices.
-
Quantum Dots
-
Electrical Steels
-
Optical Characterization
-
Magneto-Optical and Photo magnetic effects
-
Meta materials
Track 10: Ceramics and Composite Materials
The Science and technology of generating substances from inorganic, non-metallic materials within the presence of warmth or by the assistance of high purity chemical solutions is termed as Ceramic Engineering . Ceramics are crystalline materials with partly crystalline structure within the long-range order on the atomic scale. The glass-ceramics is within the short-range atomic scale with an amorphous structure. Ceramics features a unique advantage where it's are often replaced due to its heat resistant capacity. These materials are produced by the sol-gel synthesis or by hydrothermal method. Ceramic materials rise the applications in materials science, chemical, electrical and engineering . It has an exceptional usage in mining, medicine, industry , aerospace, electronics, optical and automotive industries.
Track 11: Nano Robotics
Nano robotics is an emerging technology field creating machines or robots whose components are at or near the scale of a nanometre (10−9 meters). Nanomachines are largely in the research and development phase. More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots Nano Biometric
-
Molecular Mimics
-
Lipids As Nano - Bricks And Mortar
-
self-organizing supra molecular structures
-
Biological Computing- A Protein- Based 3d Optical Memory Based On Bacteriorhodopsin
Track 12: Nanotechnology in Water Treatment
Nanotechnology engineering is an art of manipulating matter at the nanoscale . Nanotechnology offers an potential of novel nanomaterials for the treatment of surface water, groundwater, and wastewater contaminated by toxic metal ions, organic and inorganic solutes, and microorganisms. Particles of this size have unique physicochemical and surface properties that lend themselves to the novel uses. Moreover, knowledge regarding toxicological effects of engineered nanomaterials on humans and therefore the environment is presented.
Track 13: Nano Fluidics
A nanofluid is a fluid containing nanometer-sized particles, called as nanoparticles. Nanofluids have novel properties that make them potentially useful in many applications like heat transfer including microelectronics, fuel cells, pharmaceutical processes, and hybrid-powered engines cooling/vehicle thermal management, domestic refrigerator, chiller, device , in grinding, machining and in boiler flue gas cooling . All electrified interfaces induce an organized charge distribution near the surface referred as the electrical double layer. Nanofluids even have special acoustical properties and in ultrasonic fields display additional shear-wave reconversion of an event compressional wave; the effect becomes more pronounced as concentration increases.
Track 14: Surface Science and Engineering
The study of the physical and chemical process that rises by the incorporation of two phases, with solid-liquid/ solid–gas/ solid–vacuum/ liquid-gas interfaces is named as Surface Science. The actual applications of surface science in related areas are like chemistry, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and physics is recognized as the Surface Engineering. The chemical reactions at this interfaces are generally termed as Surface Chemistry and are also linked to surface engineering. The significant areas of Surface Science and Engineering are heterogeneous catalysis, electrochemistry, and geochemistry.
Track 15: Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
The field of pharmaceutical nanotechnology provides an insight into the study of characterization, synthesis and diagnostic application of materials at the nanoscale. The particular interest within the field is synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation, clinical testing and toxicological assessment of nanomaterials as drugs for various diseases. Nanotechnology is the science which deals with the processes that occur at the molecular level and the nanolength scale size. Articles should be self-contained, centred around a well-founded hypothesis and should aim to showcase the pharmaceutical/ diagnostic implications of nanotechnology. The tremendous capabilities of nanoparticles have been changed the perspective and scope of nanotechnology towards development into an adjuvant field for the remaining fields of life sciences.
Track 16: Advanced Nanomaterials
Nanomaterial’s are composed of structures at their nanoscale, usually it is achieved via specifically designed by self-assembly processes. They acquire unique optical, electronic, mechanical ,catalytic properties, magnetic, which cannot be achieved without their Nano-architecture. Nanomaterial’s enquires about adopting the approaches related to and nanotechnology materials science.
-
Novel Magnetic-Carbon Bio composites
-
Gold Nanoparticles and Biosensors
-
ZnO Nanostructures for Optoelectronic Applications
-
Thin Film and Nanostructured Multiferroic Materials.
Track 17: Smart Materials
Smart materials are often defined as materials which can significantly change their mechanical properties (such as shape, stiffness, and viscosity), or their thermal, optical, or electromagnetic properties, during a predictable or controllable manner in response to their environment. Each individual sort of smart material features a different property like volume, viscosity, and conductivity which may be significantly altered.
• Nanoplasmonic structure
• Super hard Materials
• Intelligent sensors
• Nanomaterials in Human Experience
• Amorphous Materials
• Thermodynamics of materials
• Single-molecule electronics
• Single-molecule electronics
• Transparent conducting thin films
• Future of 3D Printing.
Track 18: Materials Physics and Chemistry
Materials Chemistry provides the loop between atomic, molecular and super molecular behavior and therefore the useful properties of a cloth . It lies at the core of various chemical-using industries. This deals with the atomic nuclei of the materials, and the way they're arranged to supply molecules, crystals, etc. The length scales involved are in angstroms.
Material physics is that the use of physics to explain the physical properties of materials. It is a synthesis of physical sciences like solid mechanics ,chemistry, solid state physics, and materials science. Materials physics is taken under consideration of subset of condensed matter and applies fundamental condensed matter concepts to complex multiphase media, including materials of technological interest.
Track 19: Emerging Materials for Energy Storage
As the world-wide demand for energy is predicted to still increase at a rapid rate, it's critical that improved technologies for sustainably producing, converting and storing energy are developed. Materials are key roadblocks to improved performance during a number of important energy technologies including energy storage in batteries and supercapacitors and energy conversion through solar cells, fuel cells, and thermoelectric devices. The University of Texas at Austin is an internationally recognized leader within the development of unpolluted energy materials
Track 20: Materials Characterization and Applications
Characterization is that the crucial process within the field of Materials Science, by means of which the materials features, and properties are explored and restrained. Few basic characterization techniques that have been used for centuries include microscopy, macroscopic testing. The characterization of materials can limit them to techniques like microscopic structure and properties of materials, while others use the term to say to any materials analysis process including macroscopic techniques like mechanical testing, thermal analysis, and density calculation. The existing and future needs of human are often fulfilled by industries in accomplishing the anticipated resolution on goods.
The International Conference on Emerging Materials and Nanotechnology is the podium to share and gain knowledge from the novel technological developments in the field of science, Engineering and Technology. This conference brings together professors, researchers, scientists, students in all the areas of Material science, Engineering and Nanotechnology.
Europe accounted for 33% market share in global nanotechnology market revenue in 2015 after Americas region and is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 15.6% to reach $3.98 billion by 2021. APAC region is projected to grow at a rate of 20.9% CAGR during the forecast period 2016-2021.The analysis report informs that the global nanoparticle market is expected to reach USD 91.1 million by 2020 at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2015-2020. The market growth is being improved due to the increased emphasis on Nano technological research and funding provided by the government to carry out the R&D in this domain. The markets of China, Brazil, India and South Africa are attaining high growth prospective for the companies involved in R&D of nanotechnology and nanoparticle analyzing instruments distribution.
The global market of material science is evaluated to reach a value of $6000 million by 2020 and is expected to inscribe a CAGR of 10.2% between 2015 and 2020. The north of America holds the largest market followed by Asia-Pacific. The Europe market is estimated to be growth at a steady rate due to economic recovery in the region along with the increasing concern for the building insulation and energy savings.
The global composites market for core materials is estimated to increase from USD 1.17 Billion to USD 1.92 Billion from 2016 to 2020 respectively and a CAGR of 8.77% is expected between 2017 and 2022. There may be increase in the market of core materials as manufacturers of materials are signing supply agreements with end-use industries to hold on and improve their market in the composites.
The global market of microspheres and flexible pipe market is estimated to reach USD 6.68 Billion by 2022 with a CAGR of 9.02% between 2017 and 2022 and USD 1,111.3 Million with a CAGR of4.0% between 2017 and 2022.
The cooling fabrics market was valued at USD 1.80 Billion in 2016 and is roughly calculated to reach USD 2.94 Billion by 2021, at a CAGR of 10.3% from 2016 to 2021. The global conductive textiles market was valued at USD 1.02 Billion in 2016 and is projected to reach USD 2.11 Billion by 2021, at a CAGR of 15.6% from 2016 to 2021
Major Nanotechnology Associations around the Globe
- Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory (Brazil)
- National Center for Nano science and Technology (China)
- National Institute for Nanotechnology (Canada)
- EU Seventh Framework Programme (Europe)
- National Centre for Nano-Structured Materials, CSIR (India)
- Institute of Nano Science and Technology (India)
- Iranian Nanotechnology Laboratory Network (Iran)
- Collaborative Centre for Applied Nanotechnology (Ireland)
- Russian Nanotechnology Corporation (Russia)
- Sri Lanka Institute of Nanotechnology (Sri Lanka)
- National Nanotechnology Center (Nanotech), Thailand
- Nano medicine Roadmap Initiative (USA)
- American National Standards Institute Nanotechnology Panel (ANSI-NSP)
- Nano Ned (USA)
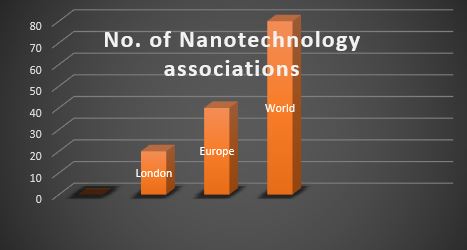
Major Material Science Associations around the Globe
- American Chemical Society (ACS)
- American Physical Society (APS)
- The Materials Information Society (ASM International)
- The Materials Research Society (MRS)
- Microscopy Society of America (MSA)
- The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS)
- Sigma Xi: The Scientific Research Society
- International Society for Optical Engineering (SPIE)
- The American Ceramic Society (ACerS)
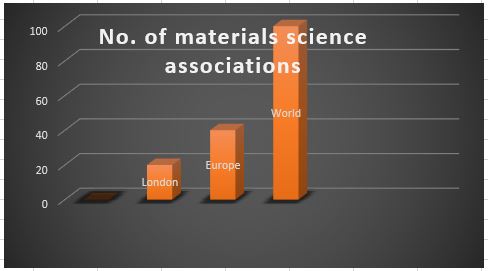
Target Audience:
- Materials Scientists/Research Professors/ Nanotechnologists
- Physicists/Chemists
- Junior/Senior research fellows of Materials Science/ Nanotechnology/ Polymer Science/
- Materials Science Students
- Directors of chemical companies
- Materials Engineers
- Members of different Materials science associations
- Members of different nanotechnology associations
- Junior/Senior research fellows of Materials Science/ Nanotechnology
Conference Highlights
- Emerging Materials and Technology
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
- Materials for Regenerative Medicine, Drug delivery and Cosmetics
- Advanced Materials
- Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering
- Polymer Science and Technology
- Advancement of Graphene Physics and 2D Materials
- Electrical, Optical, Magnetic Materials
- Ceramics and Composite Materials
- Nano Robotics
- Nanotechnology in Water Treatment
- Nano Fluidics
- Surface Science and Engineering
- Smart Materials
- Materials Physics and Chemistry
- Emerging Materials for Energy Storage
- Materials Characterization and Applications
- Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
- Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | September 30-01, 2021 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Nanomaterials & Molecular Nanotechnology
- Journal of Materials Science and Nanomaterials
- Journal of Polymer Science & Applications
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



